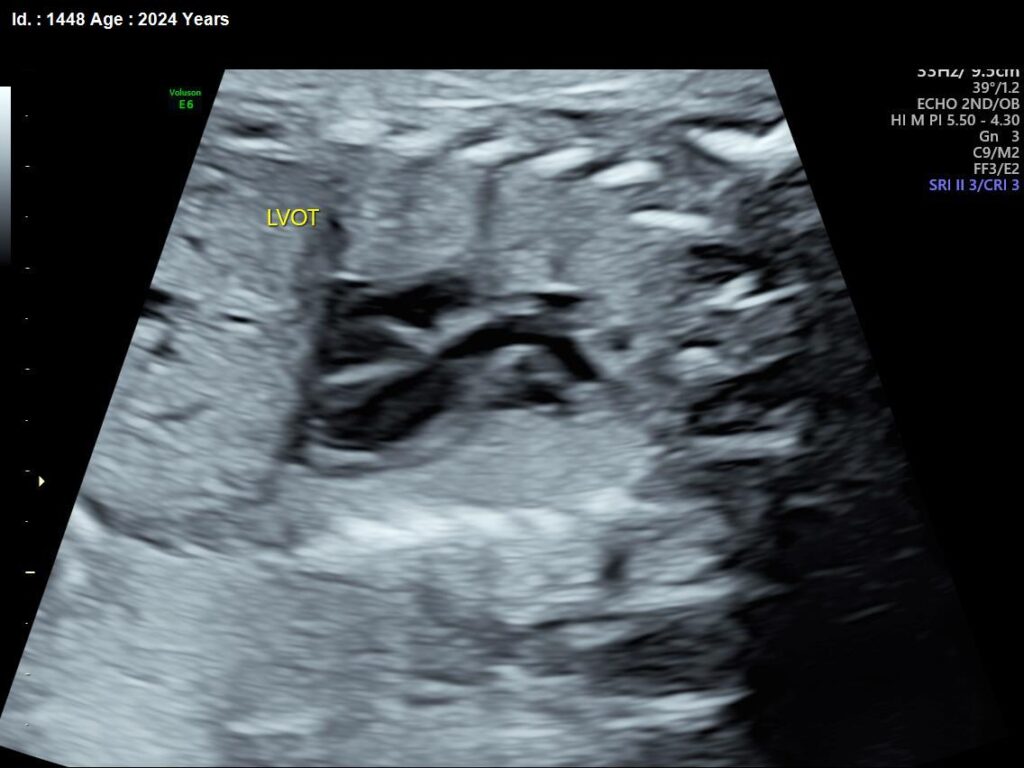
What is Unossified Nasal Bone / Absent Bone
Causes of Absent Nasal Bone
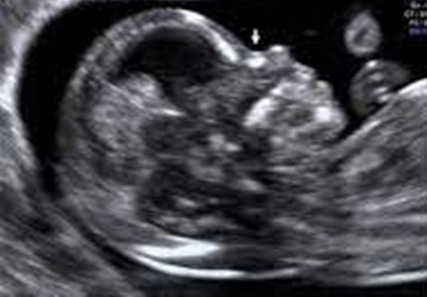
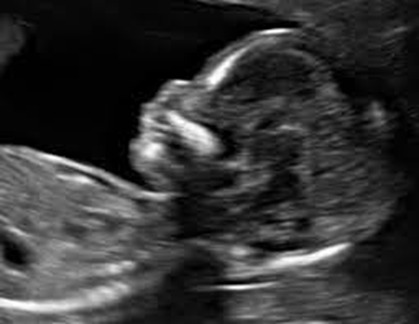
How common is Absent Nasal Bone
When can it be detected
Unossified nasal bone in first trimester
Unossified nasal bone in second trimester/20 weeks scan or third trimester
What is the significance
It can be a soft marker of Down’s syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities. Soft marker means any ultrasound sign which increases the likelihood of your baby having Down’s syndrome. More than half of babies with chromosomal abnormalities may have absent nasal bone. Normally every human being has 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs of chromosomes.
The most common chromosomal problem encountered is Down’s syndrome which is an aneuploidy of chromosome 21 where instead of two chromosomes, three are present. Affected children are mentally challenged and may have other health issues like heart defects and duodenal atresia. They also require special schools. However it is important to note that 1-2% of normal babies may also have unossified nasal bone. Hence there is no need to be alarmed when your pregnancy scan reports an unossified nasal bone.
What if i had Unossified Nasal Bone in first trimester scan and it ossifies in second trimester or Anamoly Scan
This is a common situation. Once unossified or hypoplastic nasal bone has been identified the risk for down’s syndrome /other aneuploidies remains the same even if it ossifies at a later stage.
What Next?
If unossified nasal bone is detected in first trimester, your radiologist or fetal medicine specialist will provide you one of the following options to assess your risk of a chromosomally abnormal baby
– Combined first trimester screening/ Quadruple screening: These are blood tests done in first and second trimester respectively. Sensitivity of first trimester combined screening for detecting aneuploidies is 90-95 % while of quadruple test is 60-70%.These test results can be either low risk or high risk. If low risk, then it is reassuring and we can follow up the pregnancy. If high risk, a definitive test like Chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis for karyotyping the baby is advisable.
-Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT): This is a blood test based on cell free fetal DNA which is basically DNA of the baby that circulates in maternal blood. It has a high sensitivity of 99%. Result can be low risk, high risk or no call. If low risk, pregnancy can be followed up. If high risk or no call—we have to go for direct testing.
-Direct testing: Can be either Chorionic villus sampling or Amniocentesis which is done to get the karyotype or the chromosomal make-up of the baby. In Chorionic villus sampling, tissue is taken from the placenta, while in Amniocentesis, around 20-30ml fluid is taken from around the baby. These tests are generally safe in expert hands however may carry a procedure related risk of miscarriage of around 0.3 %.
What is the further Course in Pregnancy
If the risk for having a chromosomal abnormality based on the above tests is found to be low or if karyotype shows normal result then we will routinely follow up the pregnancy at 20 weeks for anomaly scan and growth scans thereafter.
If Karyotype is abnormal, say the baby has Down’s syndrome or any other chromosomal abnormality, parents can be given an informed choice of pregnancy termination.
Does Absent / Unossified Nasal Bone Affect the baby in any way after birth? Will my baby's face have any cosmetic problem?
No. Unossified nasal bone is only an aneuploidy marker or a soft sign for Down’s syndrome. In the absence of Down’s syndrome, it does not affect the baby in any way.